Sustainable PFAS Action Network
SPAN is a coalition of industry stakeholders who advocate for responsible and science-based regulation of PFAS compounds.
Driving Science-Based Policies
America’s innovators and industries depend on the responsible management of PFAS compounds. SPAN promotes science and risk-based policies to manage the production and commercial application of PFAS compounds. While U.S. EPA has identified more than 10,000 materials that are likely to meet the broadest definition of PFAS, the number of PFAS compounds that are currently commercially manufactured or used in the United States today is closer to 700.
We support policy approaches that recognize the unique differences of these compounds and protect their acceptable use for applications that provide health, safety, security, comfort and critical technologies that are fundamental to today’s society.
Strengthening American Innovation & Competitiveness Requires an Effective Federal PFAS Management Policy
Critical steps to effective PFAS Management including characterizing, counting, and clarifying:
Characterize
Risk-Based Categorization is a Critical First Step. Adopting risk-based categorization for commercially active PFAS compounds avoids repetitive scrutiny of substances that have already been evaluated and approved. This approach will allow federal and state regulators to focus assessment efforts on a finite set of active chemistries, in accordance with the EPA’s definition.
Count
Streamline the Reporting and Regulatory Process While Facilitating Approval of Effective Alternatives. Simplification of the TSCA Section 8(a)(7) Reporting Rule would pave the way for a more practical and manageable reporting system for commercially active PFAS and PFAS-containing products.
Clarify
Focus On Commercially Active Compounds to Ensure Critical Applications are Protected. PFAS have critical applications to the 21st century economy. Permitting essential use considerations will prevent overly broad definitions from inadvertently limiting uses of PFAS compounds in industries including aerospace, semiconductors, building materials, and air conditioning technology where suitable alternatives do not exist. Providing clarity will ease the ability to pursue alternatives and also address remediation concerns. Through a meaningful “essential use” exemption for critical applications and a rapid approval process for alternatives modeled on the successful Significant New Alternatives Policy Program, the EPA can protect human health and the environment, keep our economy running, and keep America innovating.
What’s at Risk by Banning All PFAS Compounds?
Modern Life and National Defense is Made Possible by PFAS Compounds
Life-Saving Care
Medical devices like Metered Dose Inhalers and MRI machines and hundreds of active ingredients in life-saving medicines rely on or are PFAS compounds, including antidepressants and cardiovascular medications.
Energy Security
PFAS compounds enable an all-of-the-above approach to energy production and essential energy storage needs. From oil and gas production to wind and solar energy generation, PFAS are integral to energy dominance.
Military Readiness
Department of Defense reports losing access to PFAS “would greatly impact national security.” Aerospace, defense, and space industries rely on the stable performance properties in PFAS compounds in nearly all products.
Advanced Refrigerants
Refrigerants comprised of PFAS compounds refrigerate the supply chain preventing food waste and protecting our pharmaceutical cold chain while other large-scale solutions air condition millions of buildings and cars.
Automotive Safety
The automotive industry depends on high-performing PFAS compounds used in engine components such as seals and tubing, automotive sensors for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles.
Durable PPE
First responders, defense personnel, and industrial workers count the durability PFAS compounds provide in personal protective equipment to guard against extreme weather, fire, liquid chemicals, and biological hazards.
Semiconductors
As an integral component of semiconductor manufacturing, PFAS compounds underpin our digital society with the technologies that power personal devices, telecommunications equipment, and data centers.
Construction
The global construction industry uses innovative insulation products that depend on the unique properties of PFAS compounds to increase the energy efficiency of residential and commercial properties.
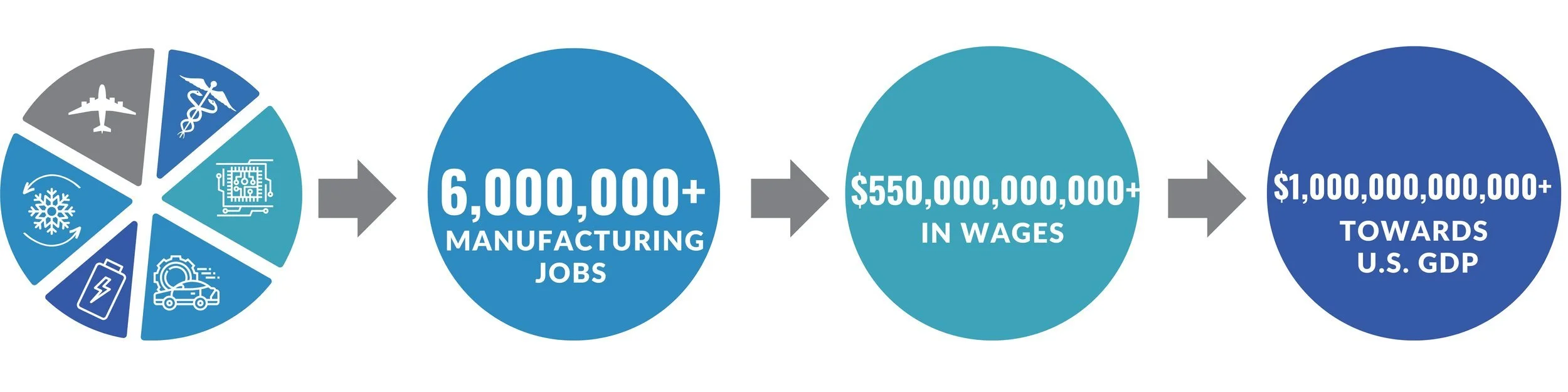
Independent Analysis: Economic Impacts of PFAS
INFORUM, a Washington-based economic consulting firm, recently studied the economic impacts of six key industries that rely on certain PFAS compounds to manufacture products. These industries support more than 6 million jobs in the United States, provide wages to their workers of more than $550 billion annually, and contribute more than $1 trillion to the national gross domestic product.
State By State Analysis:
California | Delaware | Maine | Massachusetts | Michigan | Minnesota | New Jersey | New York | Oregon | West Virginia